Blockchain
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital database where information can be added, but not removed. This data could be anything, including transactions, insurance claims, or even shares of real estate.
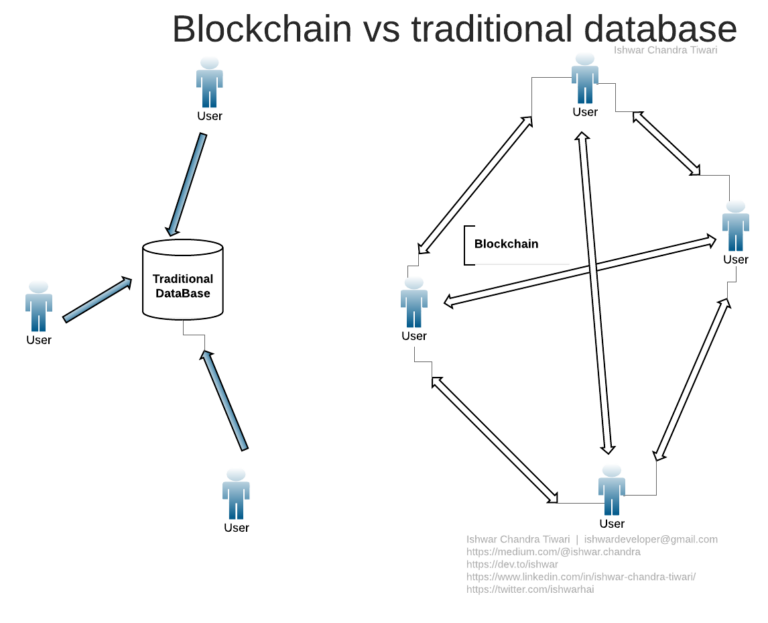
How is it different from a typical database?
There are two main differences between a typical database and blockchain; the way data is structured and the way data is stored.
Data Structure: A blockchain gathers information in groups known as blocks. Once a block has filled its storage capacity, they are closed and linked to the previous block, forming a chain (hence the name blockchain).
Data Storage: Instead of being stored on a single server, the database is distributed and stored on a large network of computers known as nodes. Every node has a full, updated copy of the ledger. This means that, unlike a traditional database, there is no single point of failure. If a node stops working, the network can still continue to function.
How does blockchain solve the issue of digital trust?
Decentralization:
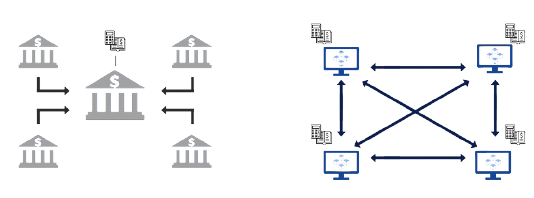
In blockchain, decentralization refers to the transfer of control from a centralized entity to a distributed network.In a traditional system, there is one central authority managing the ledger and overseeing transactions; however, on the blockchain, transactions are validated by other nodes in the system.
Decentralization is a core component of blockchain and is responsible for facilitating a trust-less system.
Fraud: In a decentralized blockchain system, fraud is practically impossible because every member in the network has a copy of the ledger. If a member attempts to modify their own record, it will be dismissed by the other individuals in the network.
Trust: The decentralized nature of blockchain means users don’t have to place their trust in third parties; rather, they trust can that the technology will manage transactions and keep their data safe.
Other Security Features:
- Utilizing cryptography
Blockchain utilizes cryptography to encrypt transactions and provide security within the network.
- Chain of Blocks
Each new block connects to the previous block forming a chain. This prevents fraud because one transaction that is tampered with will consequently disrupt the entire chain.
Transparency:
In a public blockchain, anyone can join the network and view all information on that network. In the case of cryptocurrencies, the transparency of blockchain allows users to view a history of all transactions.
This site allows you to look up Bitcoin and Ethereum transactions. You can use the search bar to search for a specific address (public key), hash, or block number. This is a great example of how transactions are transparent and able to be viewed by anyone.
Transactions:
In blockchain, the lack of third parties creates a network that operates peer-to-peer, in which transactions can happen at higher speeds and with more security and trust.
Digital Signatures:
A transaction relies on digital signatures; A system used to verify the authenticity of a digital message, document, or transaction.
A digital signature system relies on public and private keys.
A public key (sometimes called an address) is a series of letters and numbers that a user must share in order to receive funds.
A private key is a series of letters and numbers that must be kept secret as it authorizes the spending of any funds (Anyone who possesses your private keys has access to your funds).
Executing a Transaction using Asymmetric Encryption:
Asymmetric Encryption encrypts and decrypts data using public keys and private keys.
Let’s walk through an example transaction in which Alice sends Bob a classified document.
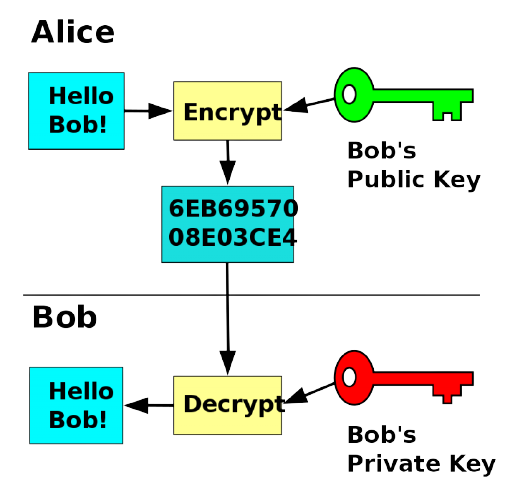
1. Alice and Bob exchange public keys
2. Alice encrypts the document using Bobs public key
Smart Contracts and dApps
Decentralized applications (dApps) are any digital application or program that runs on blockchain.
Smart contracts are programs stored on the blockchain that self-execute when predetermined conditions are met. Anyone can write a smart contract and deploy it to the network.
Smart contracts can be used to program more complex transactions like escrow transactions, trusts, and contracts, without the need for central financial institutions overseeing them.
How are Blocks Added?
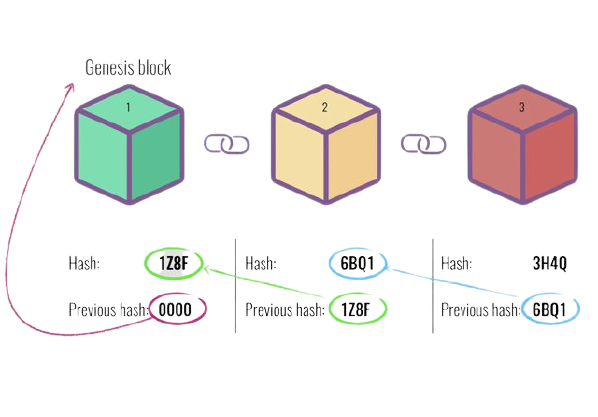
Each block contains three key things:
1. Data
2. Hash of the block
3. Hash of the previous block
Data: This data will be permanently stored on the blockchain ledger and includes all of the transaction data (sender, receiver, timestamp, transaction volume, etc.)
Hash: Hashing is a cryptographic method of converting any kind of data into a unique string of letters and numbers. Hashing provides security through encryption and creates a more efficient store of data since the hash is a fixed size.
Previous Hash: In addition to the hash, each block contains the hash of the previous block, creating a chain. This serves as a security feature because if a user modifies one transaction amount, the resultant hash would be unrecognizable, and the network would reject the fraud.
SHA-256 is the hashing algorithm used by Bitcoin. It is a one-way hashing algorithm, meaning the hash cannot be decrypted back into the original text. Try creating your own hash here!
Genesis Block: You’ll notice in the image above, Block 1 contains a previous hash of 00000. This is the hash of Block 0, also known as a genesis block, this is the first block a cryptocurrency ever mines.
How are blocks verified?
Blocks are added by having nodes verify transactions using consensus algorithms.
A consensus algorithm is a process in computer science used to reach an agreement with all the peers in the network about the present state of the distributed ledger. This protocol ensures that every new block that is added to the blockchain is the one and only version of the truth that is agreed upon by all the nodes in the network.
The main role of consensus algorithms in the blockchain is to uphold decentralization and maintain the integrity and security of the system.
Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake are the two most well-known consensus algorithms
Proof of Work (PoW): the first consensus algorithm created. It works by having participants of the blockchain (known as miners) compete to solve complex cryptographic problems. Once solved, their block is verified and added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with cryptocurrency.
Pros
- Relatively easy to implement
Cons
- Significant energy consumption
- Slow (not scalable)
